Git Branching
A Git branching strategy is a set of rules and practices for managing code changes within a Git repository. One widely used strategy is Gitflow, which defines specific branches for different stages of development.
Git Branches Flow
Each branch has its own purpose and workflow.
Master and Develop Branches
The dev branch represents the ongoing development state of the project, where features and bug fixes are integrated and tested before being released. On the other hand, the master branch reflects the stable, production-ready state of the project, containing only thoroughly tested and approved changes, typically corresponding to released versions of the software.
Feature and Bugfix Branches
The feature branches are used to develop new features or enhancements for the project. These branches allow developers to work on isolated features without disrupting the main development branches. Once a feature is complete and tested, it is merged back into the dev branch.
On the other hand, bugfix branches are created to address specific bugs or issues found in the project. After the bug fix is implemented and tested, the bugfix branch is merged back into its dev branch to incorporate the fix into the codebase.
For feature branches, it is common practice to prefix the branch name with feature/ followed by a short descriptive name of the feature being implemented. For example, if you are adding a new authentication feature, you can name the branch feature/authentication.
For bugfix branches, similar to before, the branch name is prefixed with bugfix/ followed by a descriptive name of the bug being addressed. For example, if you are fixing a bug related to user authentication, you can name the branch bugfix/authentication_issue.
Before creating any pull request to the dev branch, it is essential to ensure that the source branch (whether it is a feature or bugfix branch) is synchronized with the latest changes from the dev branch. This synchronization helps prevent conflicts and ensures that the code being merged is compatible with the current state of development.
Hotfix Branches
Hotfix branches are used to quickly address critical issues or bugs found in the production environment that can disrupt business processes. These issues require immediate attention and cannot wait for the regular release cycle. Unlike conventional deployments, changes in the hotfix branch are applied using the OTA (Over-The-Air) method. This allows users to receive critical updates within the app without the need to install updates via the App Store or Play Store. This capability is made possible by a technology called Shorebird, which is implemented in the repair workflow in our CI/CD pipeline.
For more details about the hotfix workflows, refer to the CI/CD Pipeline section.
Due to the limitations of Shorebird, hotfix branches should only
be used to deploy resolutions that are purely in .dart format files. For
other file formats, engineers must deploy using the release branch approach, click here for more details.
hotfix branches are created off the master branch to ensure that fixes are applied directly to the stable production version.
In naming the hotfix branch give the prefix hotfix/ followed by a brief description of the issue being addressed. For example, a fix for a critical security vulnerability could be named hotfix/security-fix.
Once the hotfix is implemented, it should be merged back into the master branch and dev branch. Merging into the master branch ensures that the hotfix is deployed to the production environment while merging into the dev branch ensures that the hotfix is incorporated into ongoing development work.
Release Branches
- Illustration 1
- Illustration 2
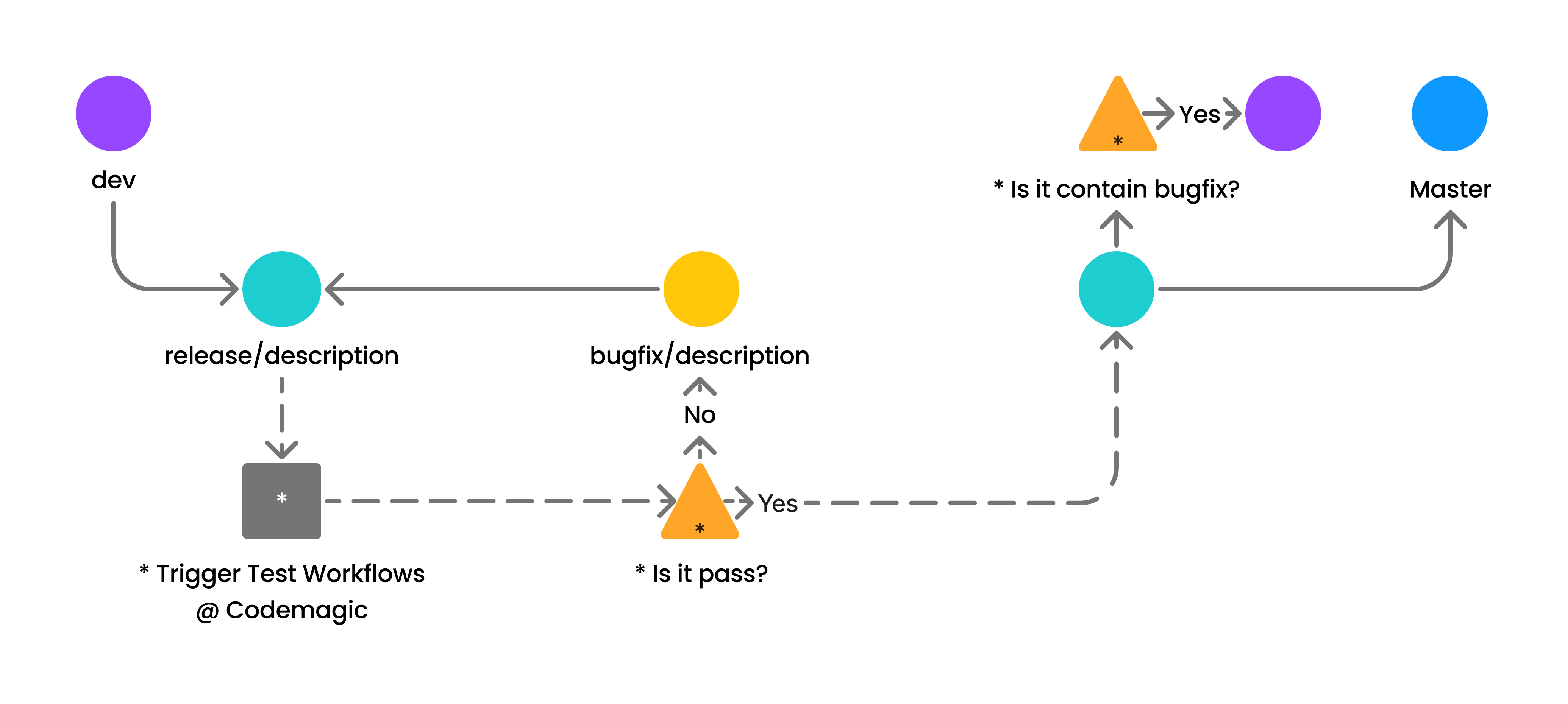
The release branches are instrumental in preparing new mobile app versions. These branches facilitate the stabilization of features and bug fixes before deployment to the production environment.
Conventionally, release branches are named with the prefix release/ followed by the version number or a descriptive name indicating the release. For instance, a release branch for version 1.0.0 might be named release/1.0.0.
When initiating a pull request from a release branch, it triggers a Test Workflow in the CI/CD pipeline at Codemagic to ensure that changes meet quality standards before deployment.
For more details on the Test Workflow, refer to the CI/CD Pipeline section.
In case of test failures in the Test Workflow, indicating issues or errors, a bugfix branch is created from the release branch. Engineers then address the identified issues by committing bug fixes to the bugfix branch. Once fixes are implemented and tested, the bugfix branch is merged back into the release branch.
The iterative process of testing, identifying issues, creating bugfix branches, and merging fixes into the release branch continues until the test workflow passes successfully. Once the release branch clears all tests, indicating stability and readiness for deployment, it can be merged into both the master and dev branches.
If there aren't any existing bugfix branches being merged into the release branch, the step of merging the release branch into the dev branch can be skipped.
Merging the release branch into the master branch deploys changes to the production environment while merging into the dev branch integrates the stable release into ongoing development efforts.
Writer: Kai
Editor: Media
Created: 25 April 2024
Updated: 25 Mei 2024
| Date | Description | Contributor | Checked |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 Mei 2024 | Renew hotfix branch definition and function, only used to send updates instantly without AppStore or PlayStore | Kai | ✅ |
| 25 April 2024 | Mobile team git branch work flow created | Kai | ✅ |