Deploy Management
Release Deployment
This section contains comprehensive steps and guidelines for successfully deploying the app to the App Store and Google Play Store.
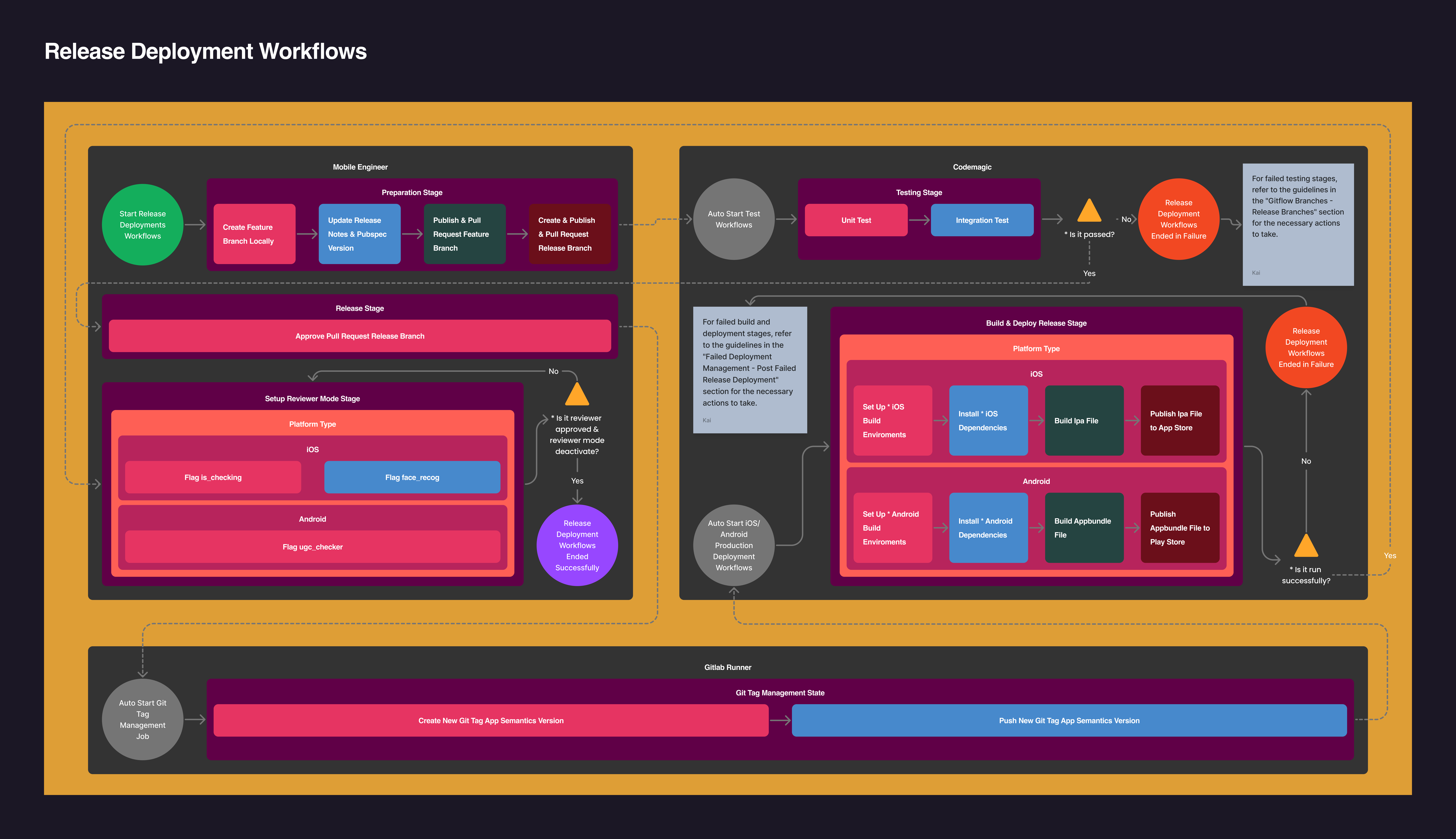
This diagram illustrates the release deployment workflows, guiding engineers through the necessary steps to deploy the latest app version to users and providing guidelines for handling any issues encountered during the process.
You must follow these three stages to support the Release Deployment workflows:
Preparation Stage
In this stage, you need to set up various important configurations for the deployments. The actions required are as follows:
Step 1.1: Create a Feature Branch Locally
- Switch the local Git branch to the dev branch, then create a new feature branch.
NOTE: Name the feature branch using the convention
feature/release_preparation_<version>, where<version>indicates the version number being prepared for release.
Step 1.2: Update Release Notes & Pubspec Version
- Update the text values in the release_notes.json file with release notes information, including any improvements, bug fixes, and new features that have been implemented.
WARNING: Do not include any emojis in the release notes. The App Store prohibits emojis, and their inclusion will result in the release submission being declined.
NOTE: Refer to Codemagic Release Notes Documentation for more information on each field in the release notes. - Update the semantic version and build number in
pubspec.yamlto reflect the significance of the changes made (improvements, bug fixes, new features).NOTE: Refer to Semantic Versioning for detailed information.
WARNING: Ensure that the build number is incremented. Failure to do so may result in deployment rejections by the Play Store. Even if all semantic versions are higher than the current version in the Play Store, a lower build number can lead to rejection.
Step 1.3: Publish & Pull Request Feature Branch
- Commit the changes and publish the feature branch to the remote repository. Create a pull request for the
featurebranch with the target set to thedevbranch.
Step 1.4: Create & Publish & Pull Request Release Branch
- Switch to the
devbranch locally and pull the latest changes from the origindevbranch. - Create a
releasebranch and publish it to the remote repository.NOTE: Release branches are named with the prefix
release/followed by the version number or a descriptive name indicating the release. For example, a release branch for version 1.0.0 might be namedrelease/1.0.0. - Create a pull request for the
releasebranch with the target set to themasterbranch.
When a pull request is created, Codemagic detects it and triggers the Test Workflows, which run a series of tests on the latest release version to ensure stability. Engineers should stand by until the Test Workflows are completed successfully, then proceed based on the Release Stage section.
NOTE: In case of
Test Workflowsfailure, refer to theGitflow Branches - Release Branchessection for necessary actions.
Release Stage
In this stage, you can execute the release process to deploy the latest version to the App Store and Play Store. The actions required are as follows:
Step 2.1: Approve Pull Request Release Branch
- Approve the pull request to merge the release branch into the target master branch.
When the pull request is approved, GitLab Runner detects the latest changes in the master branch and triggers a job named Git Tag Management. This job creates a git tag highlighting the latest version of the release in the master branch. Once the git tag is pushed to the remote, Codemagic detects this and simultaneously starts both the Android Production Deployment Workflows and iOS Production Deployment Workflows to build and deploy the latest app to the Play Store and App Store. Engineers should stand by until both workflows are completed successfully, then proceed based on the Setup Reviewer Mode Stage section.
NOTE: In case of failure during the build and deployment stages, refer to the Failed Deployment Management - Post Failed Release Deployment section for necessary actions.
Setup Reviewer Mode Stage
In this stage, engineers set up the app environment for App Store and Play Store reviewers to ensure a smooth review process, leading to the approval and publication of the latest app version. The actions required are as follows:
Step 3.1: Enable Reviewer Flags
- For iOS, set the values of
is_checkingandface_recogtofalse. - For Android, set the value of
ugc_checkertofalse.
NOTE: These fields can be found in the remote_config located in the Firebase Realtime Database.
Step 3.2: Disable Reviewer Flags
- For iOS, set the values of
is_checkingandface_recogtotrue. - For Android, set the value of
ugc_checkertotrue.
WARNING: Disable reviewer flags only when the app has been approved by the App Store or Play Store reviewer.
Hotfix Deployment
This section contains comprehensive steps and guidelines for successfully deploying critical fixes to users through OTA (Over-The-Air) deployment, bypassing the App Store and Google Play Store.

This diagram illustrates the hotfix deployment workflows, guiding engineers through the necessary steps to immediately deploy the latest critical fixes to users and providing guidelines for handling any issues encountered during the process.
You must follow these two stages to support the Hotfix Deployment workflows:
Troubleshooting Stage
In this stage, engineers set up the environment to identify and implement fixes to address critical issues.
Step 1.1: Create Hotfix Branch Locally
- Switch the local Git branch to the
masterbranch, then create a newhotfixbranch.
NOTE: Name the
hotfixbranch using the conventionhotfix/followed by a brief description of the issue being addressed.
Step 1.2: Publish & Pull Request Hotfix Branch
- Commit the changes and publish the hotfix branch to the remote repository. Create a pull request for the hotfix branch with the target set to the master branch.
WARNING:
- Ensure there are no changes other than
.dartfile formats, as this is required to enable theGit Tag Managementjob to run successfully.- Do not change any semantic versioning or build numbers in
pubspec.yamlfiles, as this would trigger aRelease Deploymentinstead.- Do not delete the hotfix branch at this step, as it will be needed later after the deployment is successfully completed.
When the pull request is approved, Gitlab Runner detects the latest changes in the master branch and triggers a job named Git Tag Management. This job first checks if there is an existing git tag containing the current app semantic version with the prefix +hotfix (e.g., 1.0.0+hotfix). If it exists, it deletes the old git tag, recreates the same git tag, and pushes it to the latest commit in the master branch. If not, GitLab Runner skips the git delete process and creates the git tag, publishing it to the remote repository.
Once the latest git tag containing the semantic version with the prefix +hotfix is detected, Codemagic triggers the iOS Hotfix Deployment Workflows and Android Hotfix Deployment Workflows to build and publish the latest patch containing critical fixes directly to the app. Engineers stand by until both workflows are completed successfully, then proceed to the Integration Changes Stage.
NOTE: In case of failure during the build and upload patch stages, refer to the
Failed Deployment Management - Post Failed Hotfix Deploymentsection for necessary actions.
Integration Changes Stage
In this stage, engineers integrate the latest critical fixes into ongoing development.
Step 2.1: Pull Request Hotfix Branch to Develop
- Create a pull request for the hotfix branch with the target set to the dev branch.
- Delete the hotfix branches after the pull request has been approved.
Failed Deployment Management
Post Failed Release Deployment
This subsection provides comprehensive guidelines for handling failed release deployments.
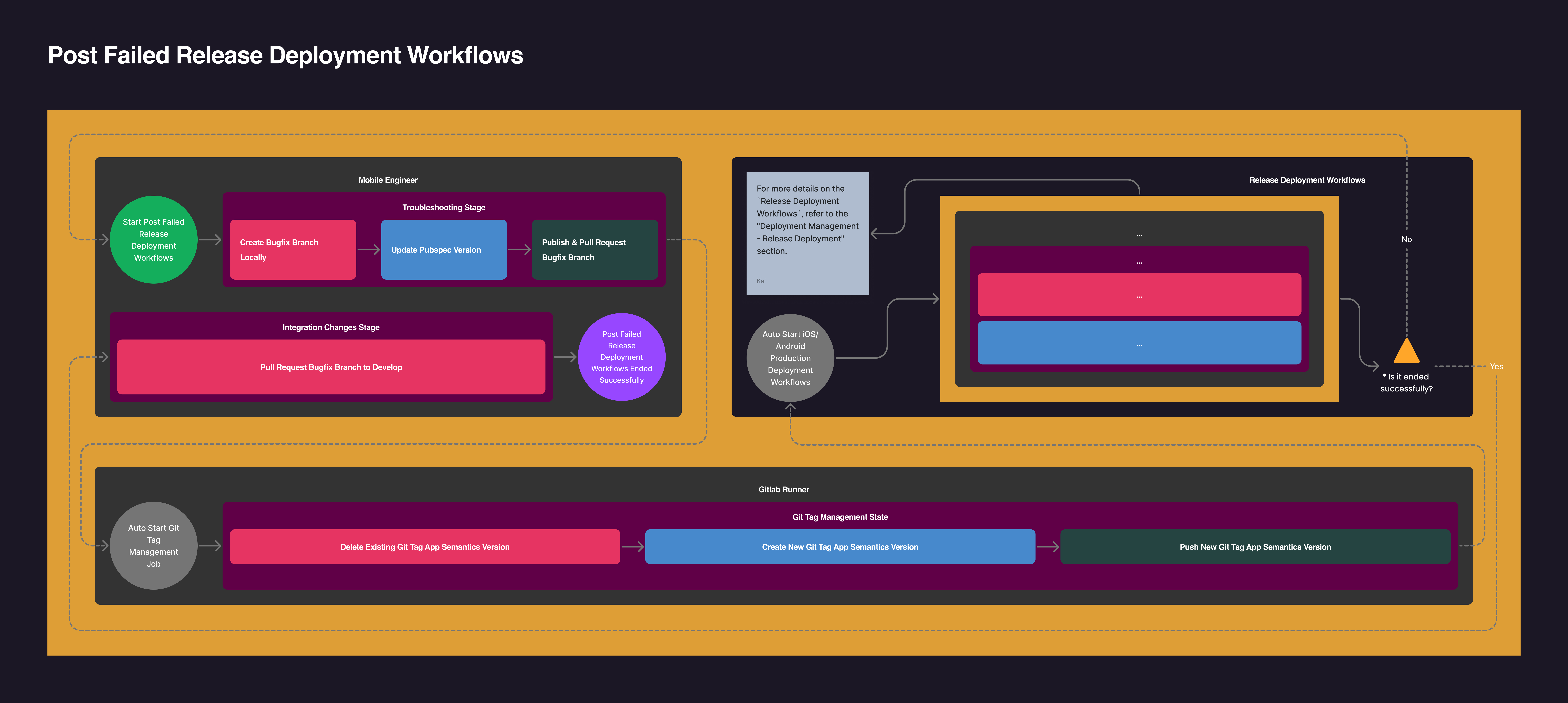
This diagram illustrates the post failed release deployment workflows, guiding engineers through the necessary steps to deploy the latest issue patches and ensure the Release Deployment workflows finish successfully.
You must follow these four steps to support the Post Failed Release Deployment workflows:
Step 1: Create a Bug Fix Branch Locally
- Switch the local Git branch to the dev branch and pull the latest changes from the remote repository.
- Create a bugfix branch from the dev branch.
NOTE: In this step, engineers address the identified issues by committing bug fixes to the bugfix branch.
Step 2: Update Pubspec Version
- Increment the current build number by one.
- Commit the updated build number changes to Git.
WARNING: Semantic versioning and build numbers are not the same. The build number is indicated by the + sign in the app version in the pubspec.yaml file.
Step 3: Publish & Pull Request Bugfix Branch
- Publish the bugfix branch to the remote repository.
- Create a pull request for the bugfix branch with the target set to the master branch.
NOTE: When the pull request for the
bugfixbranch is approved and merged into themasterbranch, GitLab Runner detects it and triggers a job namedGit Tag Management. This job deletes the previous latest git tag highlighting the latest version of thereleasein themasterbranch, then recreates the same git tag and pushes it to the latest commit in themasterbranch. The latest commit, in this case, is from thebugfixbranch that was recently merged. Codemagic then simultaneously starts both theAndroid Production Deployment WorkflowsandiOS Production Deployment Workflowsto build and deploy the latest app to the Play Store and App Store. This iterative process continues until theRelease Deployment workflowsare completed successfully. When they are, engineers can proceed to the next steps.
Step 4: Pull Request Bugfix Branch to Develop
- Create a pull request for the
bugfixbranch with the target set to thedevbranch.
NOTE: Merging the bugfix branch back into the dev branch ensures that the fixes are incorporated into ongoing development and future releases.
Post Failed Hotfix Deployment
This subsection provides comprehensive guidelines for handling the failure of critical fixes deployed through OTA (Over-The-Air) deployment.
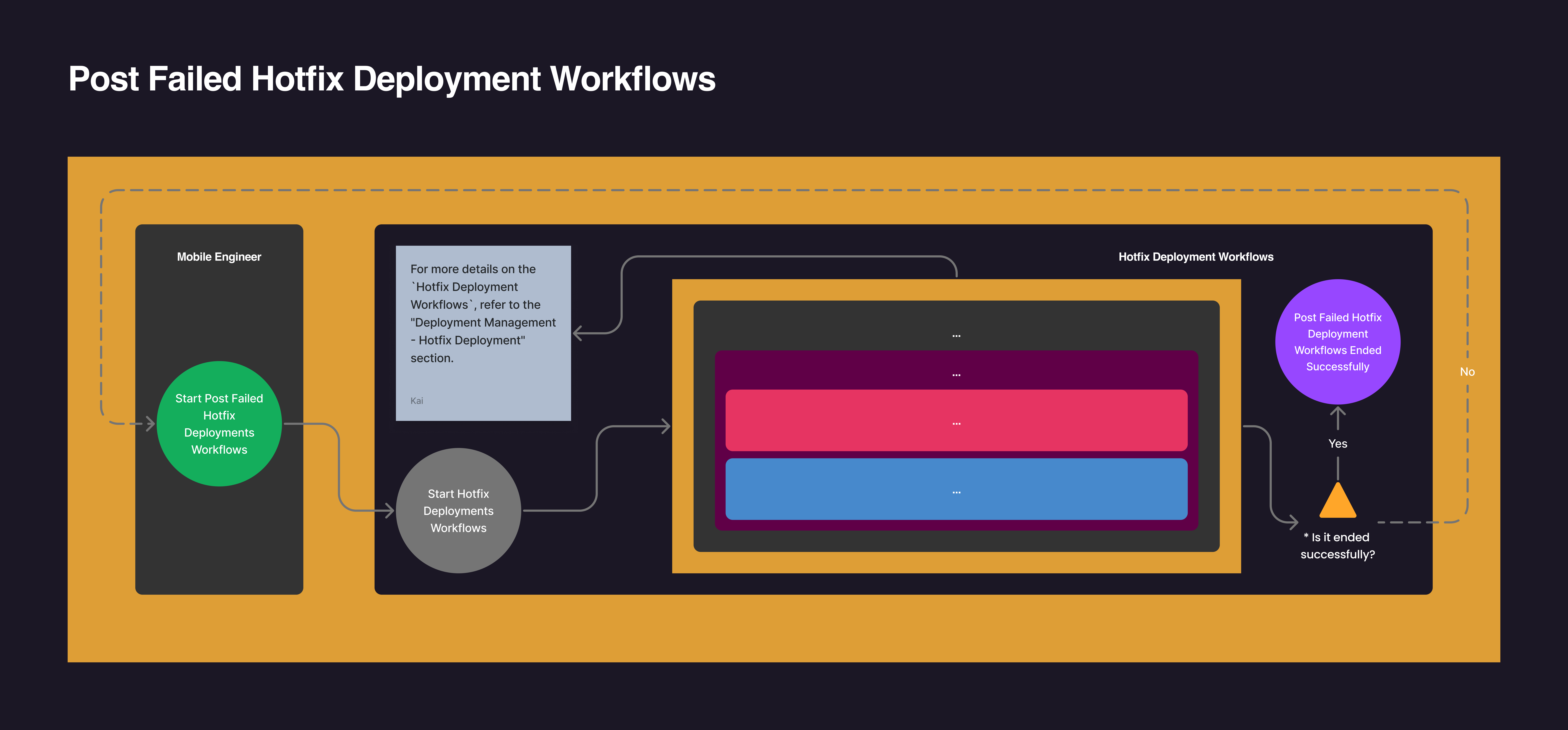
This diagram illustrates the post failed hotfix deployment workflows, guiding engineers through the necessary steps to immediately deploy the latest critical fixes and ensure the Hotfix Deployment workflows finish successfully.
When facing a failed Hotfix Deployment, the necessary action for engineers is to reiterate the entire Hotfix Deployment workflow process. Once the Hotfix Deployment workflow ends successfully, the Post Failed Hotfix Deployment process is considered complete. If the deployment fails again, reiterate the same process as highlighted in the Post Failed Hotfix Deployment guidelines.
Writer: Kai
Editor: Media
Created: 25 April 2024
Updated: 25 Mei 2024
| Date | Description | Contributor | Checked |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 Mei 2024 | - | Kai | ✅ |
| 25 April 2024 | Document created | Kai | ✅ |